Glad you come to Kennies IT, we are thrilled to have you here. As an evolving Tier-III data center dedicated to tailoring the expanding requirements of organizations nationwide. We wish you are a devoted reader and learner who has an unwavering dedication to understanding data centers and how they play a significant role in making your business streamlined. But, before going ahead in this blog post, we would like you to go to the early 90s. In the early 90s when many countries used to focus on making their arms and weapons robust.
Same as today, where the entire world is moving forward toward digitalization, countries want to invest in IT infrastructure environments together with artilleries. And when it comes to making IT infrastructure robust, data centers are paramount to secure the crucial data of several big or small companies. However, designing and constructing a data center is not as easy as it sounds. It is a complex task that needs strict adherence to different codes and standards to certify reliability, security, and efficiency.
No matter whether it’s managing massive data flows, ensuring continuous uptime, or securing sensitive data, the design and infrastructure of a data center play a vital role. This is where data center design standards and codes consolidate the best practices to aid owners in adhering to a uniform design and infrastructure pattern. These codes and standards address all the crucial aspects, from conceptual design for the facility, space planning, building construction, physical and mechanical security, to fire protection.
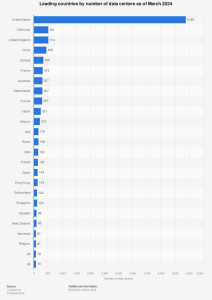
Today, in this blog, we are going to cover the essential codes and standards that govern data center design and infrastructure. From international standards and industry-specific standards to Uptime tier standards, understanding all these requirements is necessary for any organization looking to establish its data center. Before going ahead in this blog, let’s understand the statistics given by Statista on how leading countries are forwarding by a number of data centers as of March 2024.
Everything you need to know about codes and standards for data center design and infrastructure
When it comes to establishing data centers, there are specific codes and standards confirmed by national and local authorities. These codes can be implemented to save energy, increase cost savings, and data center performance. It can also certify that your data center is safe, sustainable, and stay ahead in the market. Some significant data center design standards and codes are mentioned below:
- Uptime Institute’s Tier Standard : Uptime Institute established the Tier Standards, which is a performance-based rating system. Data centers generally rely on these standards for designing, construction, and commissioning phases to determine the resilience or performance of the facility with respect to four tiers or levels of redundancy. The Tier Standards are used by data centers to build their IT equipment and power needs based on the specified redundancy configurations. According to the Uptime Institute, there are four Tier Standards.
- Tier 1 : Tier 1 refers to a general data center with basic infrastructure and IT support. A data center is rated as Tier 1 if it has an uninterrupted power supply, for potential outages or spikes, a space for IT systems, dedicated cooling systems that operate round-the-clock. Tier 1 data centers provide 99.671% uptime and are well fitted for small enterprises.
- Tier 2 : Tier 2 data centers provide 99.741% of uptime and are slightly more advanced compared to Tier 1. Tier 2 data centers have engine generators, energy storage, chillers, cooling units, UPS modules, pumps, heat rejection equipment, fuel tanks, and cells which necessarily improves the performance of systems. Each component can be removed or closed without interrupting the other components for maintenance or repair purposes.
- Tier 3: Tier 3 data centers have several paths for cooling, power, and IT systems. They are designed to function without interruption, even in critical conditions, and provide an uptime of 95.982%. With different components on standby, tier 3 data centers do not have to be closed for maintenance or repairs.
- Tier 4 : Each element within a tier 4 data center is equipped with backup systems and built to withstand faults. It provides a 99.995% uptime with multiple individual systems that are physically isolated. These individual systems protect each system from being breached.
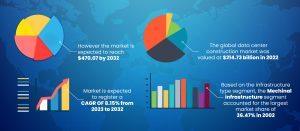
Apart from that, the global data center construction market was valued at $214.73 billion in 2022 and is expected to increase at a CAGR of 8.15% from 2023 to 2032. However the market is expected to reach $470.07 by 2032. Let’s have a look at this representation.
- ANSI/BICSI 002-2014
American National Standards Institute prescribes the Building Industry Consulting Service International 002-2014. The ANSI/BICSI 002-2014 is a reliable standard for data center design best practices, and it covers crucial fields, including planning, design, construction, and commissioning of the MEP building trades, fire protection, IT, and maintenance. BISCI-certified and skilled professionals are responsible for assessing and certifying data centers with ratings and reliability assurance.
- EN 50600: An International Standard
The EN 50600 series is a set of international standards that helps in the regular development of the data center. These standards are adapted from the concepts of UI, TIA, and BCSI standards. The ratings are issued as availability classes from 1 to 4.
The standards are classified as follows:
- EN 50600-1 General concept
- EN 50600-2-1 Building Construction
- EN 50600-2-2 Power distribution
- EN 50600-2-3 Environmental control
- EN 50600-2-4 Telecommunications cabling infrastructure
The EN 50600 series describes the different requirements or criteria for every aspect of a data center in each of the aforementioned chapters. It explains the requirements for construction, power supply, air conditioning, cabling, security systems, and more.
- Regulatory Standards
Government agencies and local authorities establish regulatory standards. These regulatory guidelines consider local and national conditions, resource availability, operational procedures, maintenance and repair requirements, and security measures. These guidelines are established to help data centers enhance their overall performance by efficiently utilizing energy and cooling systems. It also assists them in applying the top data center practices in every area.
Some of the standards are as follows:
- HIPAA – Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- SOX – Sarbanes-Oxley
- SAS 70 Type I or II – Statement on Auditing Standards
- GLBA – Gramm-Leach-Bliley
- Operational Standards
The main objective of operational guidelines is to set regulations and protocols for day-to-day operations in a data center once the facility is built. These standards are useful to ensure that the data center is maintained well and has periodic repairs, especially for crucial systems, including power and cooling units and IT systems. Moreover, these standards play a vital role in fostering data centers with sustainable energy utilization without compromising on the performance and redundancy of data centers.
Here are some significant operational standards given below:
- ISO 9000 – Quality System
- ISO 14000 – Environmental Management System
- ISO 27001 – Information Security
- PCI – Payment Card Industry Security Standard SOC, SAS70 or SSAE16
Conclusion
Sticking to codes and standards for data center design and infrastructure is vital for ensuring operational efficiency, safety, and reliability. These guidelines are established by firms like ANSI. TIA and Uptime Institute offer a framework for best practices, covering aspects from electrical systems to cooling, security, and redundancy. Thus, by implementing all these standards, businesses can overcome risks, boost performance, and conquer compliance with regulatory needs, ultimately supporting the long-term success and resilience of their data centers.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the essential standards that govern data center design and infrastructure?
Several standards govern data center design, including:
- TIA-942: Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard for Data Centers.
- Uptime Institute’s Tier Standards: Defines the reliability and availability of data centers.
- ASHRAE 90.1: Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings.
- NFPA 70: National Electrical Code, essential for electrical safety.
- ISO/IEC 27001: Focuses on information security management systems within data centers.
-
Why is adherence to codes and standards critical in data center design?
Adhering to codes and standards ensures that a data center meets industry benchmarks for safety, efficiency, and reliability. Compliance minimizes the risk of downtime, enhances the protection of data, and ensures that the facility can withstand potential hazards such as power failures, fires, or natural disasters.
-
What is the significance of the Uptime Institute’s Tier Standards in data center infrastructure?
The Uptime Institute’s Tier Standards classify data centers into four tiers, ranging from Tier I (basic infrastructure) to Tier IV (fault-tolerant infrastructure). These tiers help determine a data center’s level of redundancy, reliability, and availability, guiding organizations in selecting the appropriate infrastructure based on their specific needs.
-
How do ASHRAE standards impact data center energy efficiency?
ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers) standards, particularly ASHRAE 90.1, set guidelines for data center energy efficiency. These standards focus on optimizing cooling systems, improving power usage effectiveness (PUE), and ensuring that data centers operate efficiently while minimizing their environmental impact.
-
What role does the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) play in data center safety?
The National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) provides comprehensive regulations for electrical wiring and equipment within data centers. Adhering to NFPA 70 ensures that electrical systems are designed and installed safely, reducing the risk of electrical fires and shock hazards and ensuring reliable power distribution throughout the data center.