The Role of Data Centers in Creating Faster, User-Friendly Web Designs
The Problem & Foundation: “Why”
A website’s visual appeal is secondary if it fails to deliver speed and responsiveness. Users expect near-instant loading, smooth interactions, and uninterrupted navigation. The foundation of these experiences lies in data center infrastructure.
Data centers manage traffic routing, content delivery, and server performance globally, directly influencing how fast, stable, and seamless a website feels. Even the most visually sophisticated designs collapse without reliable backend support.
Infrastructure & User Experience
The design of the websites cannot work without a good infrastructure. Regardless of the level of colors, layouts and animations, user satisfaction is reduced because of poor performance due to slow servers. Users today expect pages to be loaded immediately on any device and network bandwidth.
A well-optimized data center guarantees a low level of delays, quick response of interactions, and low latency navigation. On the contrary, poorly developed infrastructure undermines the most carefully designed interfaces with an adverse impact on usability and interaction.
Page Speed & Conversions
Business results are directly related to site responsiveness. Research indicates that any delay of one second would boost the bounce rates and lower the conversions. Rapid loading pages build trust, promote exploration and scoring good engagement.
On the other hand, slow server response will cause loss of sessions and opportunities. The first impression line of defense in a critical first impression is developed with the data center.
Speed Physics: Latency vs. Bandwidth
To appreciate the relevance of data centers, we have to differentiate between two terms, i.e. latency and bandwidth.
Bandwidth is the volume of data that can pass through a connection, like the number of lanes on a highway.
Latency is the delay, which precedes the process of data transfer. A graphically advanced design requires a lot of bandwidth due to large assets (images, video) and a low latency due to instant responses.
Data center engineering should maximize bandwidth at the same time reduce the latency to fulfill the requirement of “faster, user-friendly”
Infrastructure to UX Metrics
Data Center Architecture
Physical data center infrastructure is required in every digital interaction. The load times, uptime and performance consistency directly depend on server hardware, network design, geographical placement and hosting.
Effective infrastructure means that the process is efficient in cases of high traffic, the downtime is minimized, and in case of interruption in services. All these have an effect on the Core Web Vitals of Google.
Advanced Cooling of the Servers
The physical hardware of the server directly affects its stability in terms of performance. Servers produce a lot of heat and the hot processor will mandate to throttle itself (thermal throttling), leading to a higher TTFB and INP.
Modern data centers use sophisticated cooling methods to prevent this:
- Hot/Cold Aisle Containment:This is used to isolate the hot exhaust air and cold inlet air, which is highly effective in terms of efficiency.
- Liquid Cooling: Direct-to-chip liquid cooling is used in high-density compute racks, which do not throttle under peak load, guaranteeing the site serves the highest speeds with heavy animations and graphics.
- Redundant Cooling Systems:There are redundant units that are immediately activated by cooling systems to ensure that temperature does not rise and performance does not deteriorate.
Core Web Vitals: Metrics That Matter
Google’s Core Web Vitals quantify real-world user experience and are tightly linked to server performance:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Measures the load time of the main visible part, the hero section in most cases. Websites can achieve this in less than 2.5 seconds by having servers that are nearer to the users as well as those with high-end hardware, which is capable of loading the main content. This will illustrate the combination of physical infrastructure, proximity, and caching strategies to have a direct influence on LCP.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
Evaluates user response to interaction, including clicks, taps and typing. High-speed, high-performance servers sustain INP less than 200ms, which guarantees a contemporary, smooth interface. INP is semantically related to backend performance, edge computing, and network optimization, demonstrating how server responsiveness is converted to interactive smoothness.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Measures visual stability in a load. Reliable infrastructure helps to avoid unforeseen changes in the elements of the UI, maintaining user experience and accuracy of interaction. CLS demonstrates how backend consistency, caching, and load balancing have a direct influence on frontend visual consistency.
3. Optimizing Delivery & Speed “How”
Proximity and Latency
Proximity of the servers to the end users has a direct impact on latency. The location of data centers will reduce latency, which contributes to greater responsiveness and create a unified experience both between devices and networks, as well as mobile connections.
This connects to Core Web Vitals and mobile performance, demonstrating that where servers are located influences LCP, INP, and CLS for all users. Web Design Company Los Angeles guide will help you find a suitable agencies for you, on the West Coast or globally.
Time to First Byte (TTFB)
TTFB is the time that is spent before the server starts data transmission. TTFB is minimized by optimized routing, high-performance servers, and strategic data center locations as the initial load speed and perceived reliability are greatly enhanced. TTFB is a key metric bridging infrastructure, hosting strategies and Core Web Vitals, and demonstrates the ability to act on the efficiency of backend in relation to frontend metrics.
Hosting Strategies
Geo-Targeted Hosting
The placement of the servers near the central user base ensures that the load time is minimized and the performance is made more stable.
The geo-targeted hosting offers a reduced latency, speedy rendering, and more interaction to users, which directly affect the conversion rates. This directly links infrastructure location to user experience and engagement creating a semantic relationship.
CDN Deployment
The CDNs duplicate the data at various locations around the world, which enables the user to access information at the closest node.
This will reduce latency, manage high traffic, and ensure consistent performance to media intensive websites. CDNs provide semantic connections between the server location and content delivery on one hand and TTFB, core web vital and UX on the other.
Edge Computing
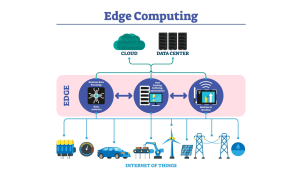
The use of edge node locations causes local storage of the static assets, shortening data travel distance and enhancing responsiveness. Edge computing as well as full interaction, animation, and real-time validations are supported as well as uniform experience across regions.
In this case, the edge computing is related to LCP, INP, CLS and mobile performance.
Image source :shutterstock
Caching & Database Optimization
Caching helps to minimize the time spent by servers to retrieve data by storing the highly used data assets near the users. Browser caching, object caching and server-side caching all minimize TTFB and increase page loads.
Optimization of databases such as query indexing and optimized retrieval allows instant delivery of dynamic content. Caching in combination with optimized databases enhances the Core Web Vitals such as LCP and INP to enable websites to appear quicker, smoother and more responsive.
Network Peering and Transit
Latency is also not only a factor of distance, but a factor of the quality of the network path. Network Peering refers to the strategic, physical linkage of two huge internet networks (ASNs). A well-peered data center reduces the count of routers between it (hop count) by a significant number of milliseconds thereby reducing the time taken to respond.
Advanced Protocols (HTTP/3, QUIC)
The network protocols of modernity enhance the transfer of data when the connection is unstable and mobile networks. The use of HTTP/3 and QUIC will minimize the loss of packets, minimize the latency, and provide more fluid user interactions. This connects protocol level infrastructure enhancements with frontend performance and Core Web Vitals.
Decentralized Data Access
Decentralized server systems spread content out to various access points, which eliminates points of failure. The routing algorithms are optimized to provide minimal number of hops, maximum throughput and dependability in delivery and keep the interface smooth with peak loads.
Mobile Performance Considerations
The users of mobile phones do not access the websites in a similar way since the speed of the network varies (3G, 4G, 5G) and the capabilities of the devices.
Close distance to data centers, CDN distribution as well as efficient backend routing minimizes latency and loading times on mobile users.
The mobile specific delivery should be optimized to guarantee that pictures, videos and dynamic content are displayed immediately and the mobile users get the mobile free frictionless experience.
| Data center architecture → hosting & CDN → TTFB → mobile UX → Core Web Vitals. |
4. Scalability & Code Support ” The Engine”
Data Center Reliability & Uptime
Good infrastructure ensures that pages load within seconds, serves the highest traffic hours and avoids crashes. It is with this reliability that performance measures such as TTFB, LCP, INP, and CLS have their basis, and there is a direct correlation to uptime and the user experience.
Tier III & Tier IV Standards
Tier III can be maintained without bringing it to a halt.
Tier IV provides complete fault tolerance that implies that everything of great concern has a separate copy.
These layers ensure high uptime rates and stability unavailable in regular configurations. This provides the user with a uniform feeling in which the pages load freely no matter what is occurring in the background.
Redundancy & High Availability
The essence of nonstop service is high availability. The absence of a backup plan leads to website breakage hence redundancy is the safety net.
Imagine it as several servers, power lines, and network paths being on call. When one of them fails another comes in immediately.
The switch is unnoticeable by the users. This is what distinguishes a site that they can withstand when the storm hits and a site which collapses each time the wind blows.(Combined with UPS & Generator, Server Stability, and Advanced Cooling for flow)
- Note: Power stability (UPS/Generator) and Server Stability/Cooling are inherent parts of achieving Tier III/IV and Redundancy, making the flow tighter here.
Load Balancing & Traffic Management
Load balancing is used in such a way that one server does not have excess traffic. The websites can easily handle a great amount of requests by spreading it over the different servers and this way; there is no problem of crashing or slowing down of the websites.
Load balancing is a complete performance strategy when it is combined with elastic scaling and CDNs. When the traffic is heavy, such as the Black Friday sales or viral content moments, the request are distributed even though to ensure that the user experience remains responsive and does not slow down unnecessarily, keeping the level of bouncing low and the response high.
Scalability and Growth
Traffic is unpredictable. Today you have 500 people on your site, the next day it becomes viral and reaches 50,000. Scalability ensures that everything remains intact regardless of the load. Scalable backend automatically adjusts to the traffic trends, so that the frontend out for the consumer is always fast.
Elastic Infrastructure
Elasticity enables the resources to expand or contract in accordance with the real-time demand. In case traffic increases, additional CPU, memory, and bandwidth are executed immediately.
As traffic declines, the system reduces in scale hence you are no longer wasting money. This makes the site run smoothly without paying excessively to the unused capacity.(Includes Cloud Scaling and Spikes Control content).
Virtualization
Elasticity is managed through sophisticated software layers like virtualization and containerization.
- Virtualization: Hypervisors are used by servers to formulate segregated Virtual Machines (VMs). This enables dynamism in the resource allocation such that when one VM requires additional CPU or RAM at a particular spiky, the system instantly takes out resources in the pooled physical resources.
- Containerization (e.g., Docker/Kubernetes): This takes the application and its environment and puts it in a unit which can be scaled horizontally with dozens of new containers being launched in seconds so that a viral moment can be handled without users noticing a hiccough.
Frontend Performance & Dynamic Content
Modern web design isn’t simple anymore.It bears high resolution pictures, video backgrounds, animations, sliders and interactivity. All these aspects require formidable back end capabilities. An effective data center will keep the site responsive even when the design is graphical so the users have a high response rate. (Combined Media-Heavy Web Designs and High-Quality Visuals here).
Advanced Frontend Techniques
Even when modern frontend optimization strategies are implemented, the data center remains the critical performance bottleneck. Advanced techniques like Server-Side Rendering (SSR), Code Splitting, and Faster Backend Interactions depend on robust backend infrastructure to achieve full effect.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) pre-renders the HTML structure of a page on the server before sending it to the user’s browser. This speeds up initial page load and improves metrics like LCP, especially for heavy JavaScript applications.
- However, SSR requires: Increased Compute Power & Fast I/O.
Code Splitting divides big JavaScript bundles into small parts that load on demand and offer reactive and efficient frontend communications. All actions of every frontend that search a product, use a sorting option, or update a cart rely on processing in the back end. Ensuring that the frontend is responsive, rather than sluggish.
Support for JS Frameworks
Such frameworks as React, Vue, and Next.js depend much on server performance to load dynamic components effectively. Quick I/O and caching data center systems contribute to making these elements faster so that navigation appears to be immediate and interactions are smooth.
Bandwidth & Throughput
Design may sound adorable, but none of it is helpful when the backbone is unable to handle data at high rates. Bandwidth and throughput determine the speed at which your content goes through a server to reach a device of the user. As soon as either of them drops, the whole site begins moving in slow motion. Powerful bandwidth and solid throughput maintain the flow to be smooth such that the heavy pages act like the lightweight pages.(Combined with Bandwidth & Visual Flow and Throughput & UX).
5. Final Considerations (“Outcome”)
Data Center Security & Integrity
People leave immediately when they feel that a site is insecure. Security is not just a technical factor but it is a psychological one. Data centers ensure a secure browsing experience by preventing attacks, data protection, and user session protection.
DDoS Protection
DDoS attacks increase false traffic on servers. Data centers with good quality have been equipped with mitigation devices that absorb attacks and leave real users unharmed. The site remains online, pages are loaded and visitors never realize that an attack is taking place in the background.
Firewalls & Encryption
Firewalls prevent illegal access. During data transfer between the server and the browser, it is safeguarded by encryption. Accounts and payments are secured by secure sessions. Feeling that their information has been secured, the users will be confident enough to operate on the site, take more time, and make a purchase.
Strong Security & Bounce Rates
A sketchy site is nothing that passengers can fear more. Good security will ensure that there are no fears among the visitors on the site to explore the site. Such trust will have a direct positive impact on engagement and a decrease in bounce rate (Along with Data Integrity).
Emerging Data Center Technologies
The demands by the user-friendly design are ever changing. The modern infrastructure providers are not confined to the current standards they are looking forward to cater to the next generation of web experience.
- AI-Driven Load Balancing: Algorithms that forecast traffic trends and automatically redistribute resources in advance, preventing a spike, are known as AI-driven load balancing.
- Edge AI/ML Processing: Running small Machine Learning models on edge nodes. This enables real-time, hyper-personalized user experiences (such as instant content recommendations or personalized layouts) without the round-trip latency to a central cloud, which improves INP on dynamic sites dramatically.
Industry Use Cases
Different industries rely on websites differently, but they all need top-tier performance. Here’s how data centers shape UX across high-impact sectors:
- E-Commerce Speed: Speed is money in ecommerce. Data centers are stable enough when they are under pressure and hence, users can browse, compare and purchase products without hitches even during mega sales.
- SaaS Performance: SaaS tools are based on real time performance. All the apps will behave well and the user is either editing documents, analyzing graphs, or working with financial data; low-latency servers will make sure that the applications perform well regardless of the task.
- Media & Streaming: News websites, streaming services and global media will be unable to operate without CDNs and optimized backend servers. These systems provide the content in the closest node thus allowing a very fast streaming with minimum buffering.
Infrastructure Checklist
To prevent the disasters of performance during the web development, a successful web development company uses a planning checklist, which may include:
- Growth bandwidth forecasting.
- Power and network redundancy planning.
- Global delivery through integrating CDN.
- Distributed load balancing amongst servers.
- The use of caching layers in order to accelerate heavy content.
- Security stacking of secured sessions.
- To identify weak points, performance stress testing.
This is the planning that makes the site quick and prepared to grow in the future.
Choosing the Right Web Design Partner
The core of performance with regard to the web is a data center. A powerful backend makes your site load quicker, is more responsive, remains secure, and a reliable experience even in high traffic conditions. This is a trusted reliability that generates repeat users. Data centers are high-performance, stable, secure, replicable, and easy to see, all of which the present-day web design must shine.
There is no way a strategic company will not match the great visuals with the great planning of the back end. That is the way you have a site that does not only look good but has the functionality of a high-end product.